Selfie Capture
About this guide
This guide is designed to help you implement the Android SDK quickly and easily. Basic concepts, examples of SDK implementation and how to interact with the biometric engine REST APIs are provided.
Through this guide, you can:
- Implement camera play and image capture;
- Manipulate the return data;
- Use the SDK feedback with the biometric engine APIs.
Before you begin
Make sure you followed the step-by-step instructions for installing and importing the SDK following this guide. It is also important to consider the features available in this SDK, as explained on the overview page.
Available resources
The Android SDK offers a component for capturing a selfie containing a silhouette that helps the user to position themselves correctly for the photo. Selfie capture can be done in five different ways, each way with a different camera mode:
SELFIE CAMERA WITH MANUAL CAPTURE
In this type of experience there is a capture silhouette to help the user position their face correctly. After positioning themselves correctly, the user must click on a button to capture the selfie.
The SDK does not perform any kind of validation of what is being captured. If the captured image does not have a biometrically valid face, the encrypted is refused by the biometrics engine backend APIs.

SELFIE CAMERA WITH SMART CAPTURE
In this type of experience, the user face is automatically identified through the computer vision algorithms and help them to position themselves correctly within the capture silhouette. After positioning yourself correctly, the image is automatically captured.
By helping the user to frame their face in the capture area, this option can reduce problems when sending the encrypted to the biometric engine backend APIs.

SELFIE CAMERA WITH FACETEC PROOF OF LIFE
In this type of experience, after centering the face on the capturing silhouette, the user is instructed to perform a simple movement of approaching the face, which are followed by computer vision algorithms to ensure that the user is really taking the photo at that moment.
By requiring the user to move, this type of capture has an extra layer of security against fraud. With the automatic capture, the image is captured without the need for the user to press a button. In this way, there is a tendency to reduce problems when sending encrypted to the biometric engine backend APIs.

Activation of the functionality can be verified on the customer portal, as explained in this article.
HOW TO CUSTOMIZE INTERACTIVE LIVENESS WITH YOUR LOGO
For an authentication experience more associated with your brand, you can insert and customize the logo in real time.
- Add the image file to the drawable folder of your app with the following name:
unico_custom_footer_logo. Allowed extensions: .jpg, .png, and .svg.
The folder and file names need to be correct. Otherwise, the implementation will not work.
After completing the steps, the customization is ready and you can see your logo in the interactive Liveness capture frame.
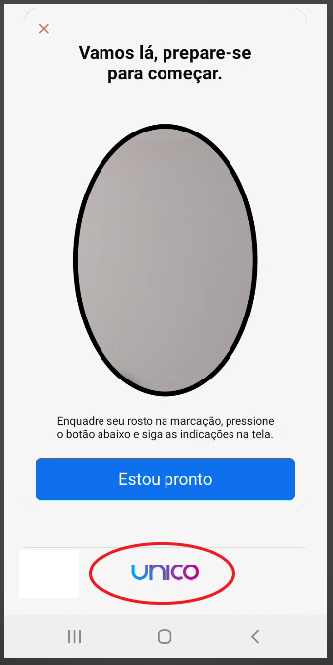
Your logo should appear at the bottom of the screen as shown below:
CUSTOMIZE LANGUAGE
It's possible to configure the experience of informative messages in capture frames by changing their language. Use the enumeration LocaleTypes which contains the following values:
Here's how to implement it in the example below:
- Java
- Kotlin
unicoCheck.setLocale(LocaleTypes.EN_US);
unicoCheck.setLocale(LocaleTypes.EN_US)
REAR CAMERA WITH MANUAL CAPTURE
This information will be available soon.
REAR CAMERA WITH SMART CAPTURE
This information will be available soon.
Implementation
By following this step-by-step guide, you have the full potential of the SDK embedded in your Android application.
INITIALIZE THE SDK
Create an instance of the builder (Generated through the IAcessoBioBuilder interface), providing as a parameter the context in question and the implementation of the AcessoBioListener class.
The implementation of this class is very simple and can be done with a few lines of code. All you need to do is instantiate the builder informing the context and environment in question and override the callback methods with your application's business logic:
- Java
- Kotlin
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private AcessoBioListener callback = new AcessoBioListener() {
@Override
public void onErrorAcessoBio(ErrorBio errorBio) { }
@Override
public void onUserClosedCameraManually() { }
@Override
public void onSystemClosedCameraTimeoutSession() { }
@Override
public void onSystemChangedTypeCameraTimeoutFaceInference() { }
};
private IAcessoBioBuilder acessoBioBuilder = new AcessoBio(this, callback);
}
internal class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val callback = object : AcessoBioListener {
override fun onErrorAcessoBio(errorBio: ErrorBio?) { }
override fun onUserClosedCameraManually() { }
override fun onSystemClosedCameraTimeoutSession() { }
override fun onSystemChangedTypeCameraTimeoutFaceInference() { }
}
private val acessoBioBuilder: IAcessoBioBuilder = AcessoBio(this, callback)
}
ENVIRONMENT CONFIGURATION
Configure the environment that will be used when running the SDK. Use the enumerated Environment, which contains the following enumerations:
Environment.PROD: for the Production environment
Environment.UAT: for the Testing environment
See how to implement it in the example below:
- Java
- Kotlin
acessoBioBuilder.setEnvironment(Environment.UAT);
acessoBioBuilder.setEnvironment(Environment.UAT);
IMPLEMENT CALLBACK FUNCTIONS
Note that the work of implementing the AccessBioListener class is, to a large extent, configuring the callback methods. Each method is called in a specific situation back from the SDK.
Just overwrite the methods exemplified in the previous step with the business logic of your application.
This method is invoked whenever any implementation error occurs when using any of our methods:
onErrorAcessoBio(ErrorBio errorBio)
When invoked, the method receives a parameter of type ErrorBio that contains details of the error. Learn more about the ErrorBio type in the references section.
This method is always invoked when the user closes the camera manually, for example, when clicking on the "Back" button:
onUserClosedCameraManually()
This method is invoked once the maximum session time is reached (Without capturing any images):
onSystemClosedCameraTimeoutSession()
It can be configured in builder through the setTimeoutSession method. This method should receive the maximum session time in seconds. You can change your user's maximum session time when using the face detection feature (Selfie camera with smart capture). If it exceeds the time determined in your process to capture the photo, you can present some customizable message or instruction to the user. The default value is 40 seconds and its minimum value is also 40 seconds.
This method is invoked as soon as the maximum time for detecting a user's face is reached (Without having anything detected). In this case, the camera mode is automatically changed to the manual capture mode (Without the smart capture silhouette):
onSystemChangedTypeCameraTimeoutFaceInference()
The maximum capture time when using face detection (Smart Capture Selfie Camera) is 13 seconds. If the user finds any difficulty in capturing the photo through the face detection and exceeds the time determined in its process, the capture is automatically changed to manual, with the aim of facilitating the action for the user (TimeoutToFaceInference).
All the above methods must be created in the way indicated in your project (Even without any logic). Otherwise, the project does not compile successfully.
SET CAMERA MODE
As explained earlier, there are five camera capture modes available. If you are not using the Selfie camera with FaceTec proof of life mode, in this step you can choose among the modes: Selfie camera with manual capture, Selfie camera with smart capture, Rear camera with manual capture or Rear camera with smart capture.
The SDK has smart framing and auto capture configured and enabled by default. To use the selfie camera with manual capture, disable both features through the setAutoCapture and setSmartFrame methods.
The following examples demonstrate how you can configure each of the camera modes:
SELFIE CAMERA WITH MANUAL CAPTURE (MANUAL MODE)
By default, the SDK has smart framing and auto-capture enabled. In this case, to use manual mode both settings related to Smart Camera must be turned off through the setAutoCapture and setSmartFrame methods:
- Java
- Kotlin
UnicoCheckCamera unicoCheckCamera = acessoBioBuilder
.setAutoCapture(false)
.setSmartFrame(false)
.build();
val unicoCheckCamera: UnicoCheckCamera = acessoBioBuilder
.setAutoCapture(false)
.setSmartFrame(false)
.build()
Even using manual capture mode, it is possible to use Smart Frame. In this case, the colored signal on the silhouette, to identify the framing of the face and then enable the button. To do this, just set setAutoCapture(false) and setSmartFrame(true).
SELFIE CAMERA WITH SMART CAPTURE (SMART CAMERA)
By default, the SDK has smart framing and auto-capture enabled. If you decide to use this camera mode, you do not need to change any settings.
If the camera settings were previously changed in your App, you can restore them using the setAutoCapture and setSmartFrame methods:
- Java
- Kotlin
UnicoCheckCamera unicoCheckCamera = acessoBioBuilder
.setAutoCapture(true)
.setSmartFrame(true)
.build();
val unicoCheckCamera: UnicoCheckCamera = acessoBioBuilder
.setAutoCapture(true)
.setSmartFrame(true)
.build()
It is not possible to implement the setAutoCapture(true) method with the setSmartFrame(false) method, that is, it is not possible to maintain the automatic capture without the Smart Frame, as it is the one that performs the smart framing.
If using this mode, the camera mode setting becomes irrelevant as this mode offers a pre-set experience that cannot be changed.
However, it is suggested that you configure a camera type in your builder (As described in this step), because if you disable the Liveness with Interaction mode on the instance and generate a new JSON, you don't need to change yours code.
If you want to use this mode, it is necessary that in the APIKey settings, the field Type of camera in the SDK is selected with the option Rear.
PERSONALIZATION THE CAPTURE PROCESS
This is an optional step, but highly recommended so that the capture process has your company's visual identity.
It is possible to customize some objects of the frame according to the camera mode used, through the setTheme() method.
Supported types for color representation are Color Resource or String containing the hex code of the color. Ex: R.color.red ou #FF0000
All methods are available below:
- Java
- Kotlin
IAcessoBioTheme unicoTheme = new IAcessoBioTheme() {
@Override
public Object getColorBackground() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorBoxMessage() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorTextMessage() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorBackgroundPopupError() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorTextPopupError() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorBackgroundButtonPopupError() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorTextButtonPopupError() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorBackgroundTakePictureButton() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorIconTakePictureButton() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorBackgroundBottomDocument() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorTextBottomDocument() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorSilhouetteSuccess() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorSilhouetteError() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
@Override
public Object getColorProgressBar() {
return R.color.your_color;
}
};
acessoBioBuilder.setTheme(unicoTheme);
val unicoTheme = object: IAcessoBioTheme {
override fun getColorBackground() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorBoxMessage() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorTextMessage() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorBackgroundPopupError() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorTextPopupError() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorBackgroundButtonPopupError() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorTextButtonPopupError() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorBackgroundTakePictureButton() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorIconTakePictureButton() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorBackgroundBottomDocument() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorTextBottomDocument() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorSilhouetteSuccess() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorSilhouetteError() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorSilhouetteNeutral() = R.color.your_color
override fun getColorProgressBar() = R.color.your_color
}
acessoBioBuilder.setTheme(unicoTheme)
It is also possible to make customizations statically, in your colors.xml file add the following code:
<color name="unico_color_background"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_silhouette_success"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_silhouette_error"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_silhouette_neutral"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_box_message"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_text_message"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_background_popup_error"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_text_popup_error"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_background_button_popup_error"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_text_button_popup_error"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_background_take_picture_button"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_icon_take_picture_button"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_background_bottom_document"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_text_bottom_document"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_button_cancel"> #YourColor </color>
<color name="unico_color_progress_bar_capture"> #YourColor </color>
Please, refer to the available personalization methods by camera mode.
SELFIE CAMERA WITH MANUAL CAPTURE
In this camera mode it is possible to personalize:

SELFIE CAMERA WITH SMART CAPTURE
In this camera mode it is possible to personalize:

SELFIE CAMERA WITH FACETEC PROOF OF LIFE
In this camera mode it is possible to personalize:



REAR CAMERA WITH MANUAL CAPTURE
This information will be available soon.
REAR CAMERA WITH SMART CAPTURE
This information will be available soon.
CONFIGURE CREDENTIALS
You must enter the SDK Key as described in EMBARKING CREDENTIALS INTO YOUR PROJECT
IMPLEMENT LISTENERS FOR CAMERA EVENTS
The camera's aperture method, which is called in the next step, needs to know what to do if it manages to capture an image successfully or if it has an error in the process. It is necessary to inform "what to do" to the method of opening the camera through the implementation of listeners that is called in situations of success or error.
Through the configuration of the listeners, you can specify what happens in your App in situations of error (onErrorSelfie method) or success (onSuccessSelfie method) in capturing images.
There were the following changes:
- From the prepareCamera method which was previously prepareSelfieCamera;
- From the CameraListener class that was previously SelfieCameraListener;
- From the UnicoCheckCameraOpener.Camera object that was previously UnicoCheckCameraOpener.Selfie.
To configure the listeners, it is necessary to implement:
- Java
- Kotlin
iAcessoBioSelfie cameraListener = new iAcessoBioSelfie() {
@Override
public void onSuccessSelfie(ResultCamera result) { }
@Override
public void onErrorSelfie(ErrorBio errorBio) { }
};
unicoCheckCamera.prepareSelfieCamera(unicoConfig, new SelfieCameraListener() {
@Override
public void onCameraReady(UnicoCheckCameraOpener.Selfie cameraOpener) {
cameraOpener.open(cameraListener);
}
@Override
public void onCameraFailed(String message) {
Log.e(TAG, message);
}
});
val cameraListener: iAcessoBioSelfie = object : iAcessoBioSelfie {
override fun onSuccessSelfie(result: ResultCamera?) {}
override fun onErrorSelfie(errorBio: ErrorBio?) {}
}
unicoCheckCamera.prepareCamera(unicoConfig, object : CameraListener {
override fun onCameraReady(cameraOpener: UnicoCheckCameraOpener.Camera?) {
cameraOpener?.open(cameraListener)
}
override fun onCameraFailed(message: String?) {
Log.e(TAG, message)
}
})
The implementation of these methods listeners must be done through an instance of the iAcessoBioSelfie class.
PREPARE AND OPEN THE CAMERA
To proceed with opening the camera, you must first prepare it using the prepareCamera method. This method receives as a parameter the implementation of the CameraListener class, the class or the JSON with the credentials, generated in this step.
When the camera is ready, the onCameraReady event is triggered, which receives an object of type UnicoCheckCameraOpener.Camera as a parameter.
It is necessary to override this method, opening the camera with the object received through the open() method. The open() method should receive the listeners configured in the steps above as a parameter.
ONSUCCESSSELFIE METHOD
When performing an image capture with success, this method is invoked and returns an object of type ResultCamera that is used later in the call of the REST APIs:
public void onSuccessSelfie(ResultCamera result) { }
The ResultCamera object returns 2 attributes: Base64 and Encrypted:
- The Base64 attribute can be used if you want to display a preview of the image in your app;
- The Encrypted attribute must be sent when calling the unico | check (Detailed in the next section).
The Encrypted attribute is strictly intended for sending the image through the Unico APIs. You should not open and serialize this attribute, as its characteristics may change without notice. Its use must be exclusive in interactions with the APIs to guarantee the data integrity and security. Unico is not responsible for any damages arising from this practice, since the changes may occur unpredictably.
ONERRORSELFIE METHOD
When an error occurs in the image capture, this method is invoked and returns an object of type ErrorBio:
public void onErrorSelfie(ErrorBio errorBio) { }
About ErrorBio types in the References section of this SDK.
If you need to convert base64 to bitmap, the standard way does not work for Android. You need to perform the split from the comma(,) for it to work. If you want to know more, read the following article How to convert a Base64 string into a Bitmap image to show it in an ImageView?.
CALL THE APIS
Capturing the images is just the first part of the journey. After capturing the image, it is necessary to send the generated Encrypted to the APIs, selecting one of the available flows detailed in Flows.
For security reasons, the interval between generating the Encrypted and sending it via one of the available flows must be a maximum of 10 minutes. Submissions made beyond this period will be automatically rejected by the API.
Any concerns?
Didn't find something or still need help? If you are already a customer or partner, you can contact us through Help Center.